Expanded foam packaging has grown as a potential option to protect industrial goods during the distribution cycle. Shocks, drops, vibrations, and rough handling all constitute dangers for the integrity of goods. However, using the right type of molded foam packaging can safeguard products against such risks, while also being cost-efficient and reducing the packaging carbon footprint.
What has expanded foam packaging?
Expanded foam packaging is a very versatile type of packaging that adapts to products’ sizes and shapes through the use of custom configurations. Also known as molded foam, this material can be created (molded) with specific products in mind so that it fits exactly the packaged product, surrounding it, filling the container, and creating a cushion that protects it.
Expanded foam packaging is ideal for products with odd shapes, corners, edges, or elements that protrude, as it can be custom-made to adapt to all of them. This is the reason why it’s widely used in the industrial sector, including a wide range of products from electronics to the automotive industry.
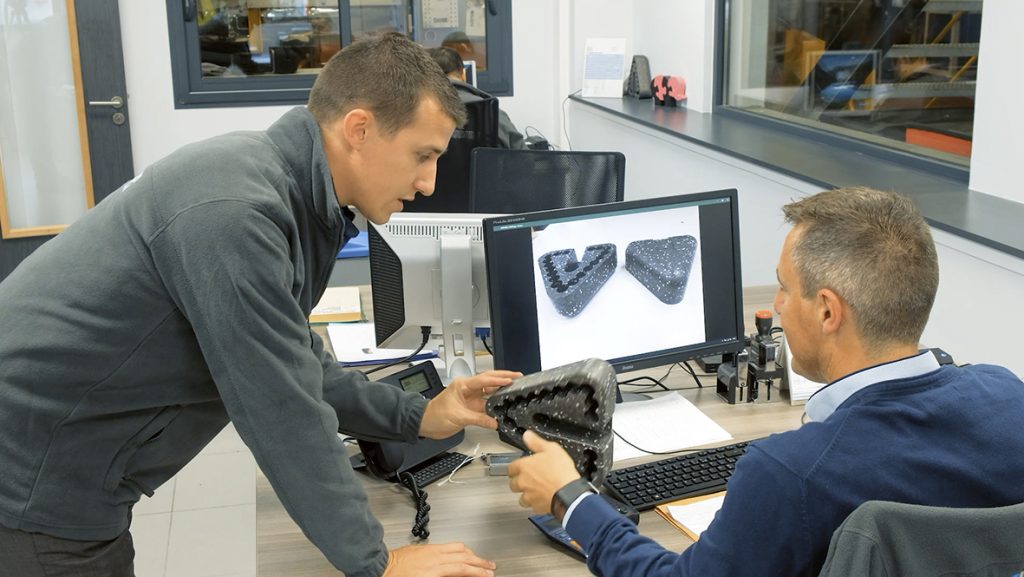
Experts in foam molding technologies can create individually designed expanded foam packaging to ensure perfect storage and transportation.
You might also be interested in: How to improve HVAC efficiency with expanded foam
Innovative features of expanded foam packaging
Expanded foam packaging: the importance of lightness and protection
Molded foam packaging is extremely lightweight compared to other packaging options. This is why one of the main benefits that the industry sector can obtain by using expanded foam packaging is a reduction in costs: transportation costs are reduced as shipping units weigh less by using this lightweight material.
On top of this, companies can benefit from cost savings derived from fewer accidents and product depletion, as expanded foam packaging options offer effective protection for goods.
Materials and composition of foam packaging
Expanded foam packaging can be made of several different materials. While traditional options have included polyurethane and polyethylene foams, the packaging industry has discovered the potential of EPP and EPS for protection in recent years.
EPP (expanded polypropylene) and EPS (expanded polystyrene) are both packaging materials made of plastic beads. 98% of both materials’ composition is air and both present some extraordinary advantages:
- Impact resistance and shock absorption, providing the right protection even for very fragile materials
- Very durable
- Lightweight
- Great thermal insulators
- Sustainable: both are 100% recyclable and EPP can be used for returnable packaging, as it is reusable and preserves its mechanical performance even in the long term
Reducing packaging carbon footprint
Expanded foam packaging helps to reduce a company’s packaging carbon footprint in many ways:
- As it’s custom made, it’s optimized to minimize packaging waste and unnecessary packaging production
- Selecting EPP and EPS as materials for expanded foam packaging guarantees it can be recycled
- Expanded foam packaging makes logistics as efficient as possible, avoiding the return of products and unnecessary extra transportation
You might also be interested in: Plastic injection molding solutions
Eco-innovation to contribute to a circular economy
Expanded foam packaging made from EPS and EPP constitutes an innovative, sustainable option for industrial companies who wish to reduce their packaging carbon footprint. Made of 98% air, neither material is made using toxic substances.
On top of these advantages, there are at least two outstanding benefits of using EPS and EPP for companies that wish to make a move towards the green economy:
Recycling process
While EPS and EPP are non-biodegradable, both materials are 100% recyclable and non-pollutant. Besides, they increasingly incorporate recycled polystyrene from production and worksite remains, reintroducing these materials into a new lifecycle and minimizing waste. This is done through reprocessing plants, which are progressively being introduced across the globe.
The goal is to generate a circular economy model, where durable plastics such as EPS and EPP have a longer lifecycle and are not just used once. This is especially the case of EPP packaging, which companies can reuse with no additional processes.
Biosourced and biodegradable foams
Expanded foam packaging can also be conceived as a non-petro-sourced material: NEOPS®, developed by Knauf Industries, is an alternative to expanded polystyrene (EPS) that constitutes the first certified foam from renewable sources made out of vegetal sources.
The material was born out of a collaboration between our ID packaging lab and the producers of raw materials and is manufactured according to the concept of biomass balance developed by the REDcert certification (a new standard on the use of sustainable biomass in the chemical industry).
This certifies NEOPS® as a cellular, non-petro-sourced material, which comes from non-food renewable resources (green waste). This innovation reduces the use of fossil raw materials and allows companies to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions (CO2) by at least 30%.
NEOPS® is 100% recyclable through the same channels as EPS (our KNAUF Circular model) and its technical performance is identical to EPS, only presenting a better environmental impact. Additionally, different material grades are available with improved performance for thermal, fire resistance, shock absorption, and food contact.
With our EPS and EPP solutions, as well as our innovative non-petro-sourced material NEOPS®, we confirm our commitment to developing sustainable, innovative packaging materials for the industrial sector.
Learn more about our expanded foam packaging options and how Knauf Appliances can help you design, prototype, test, and apply eco-innovation.