EPS - Expanded Polystyrene
What is EPS
EPS is a highly versatile closed-cell bead foam widely used in industrial applications. It is produced by expanding polystyrene beads with a steam process, which transforms them into fine spherical particles composed of 98% air and only 2% polystyrene material.
Due to its characteristics it is a safe and environmentally neutral material and presents tons of benefits that make it go a step further than the vast majority of other types of plastics.

How to process EPS
EPS production process consists in three main steps:
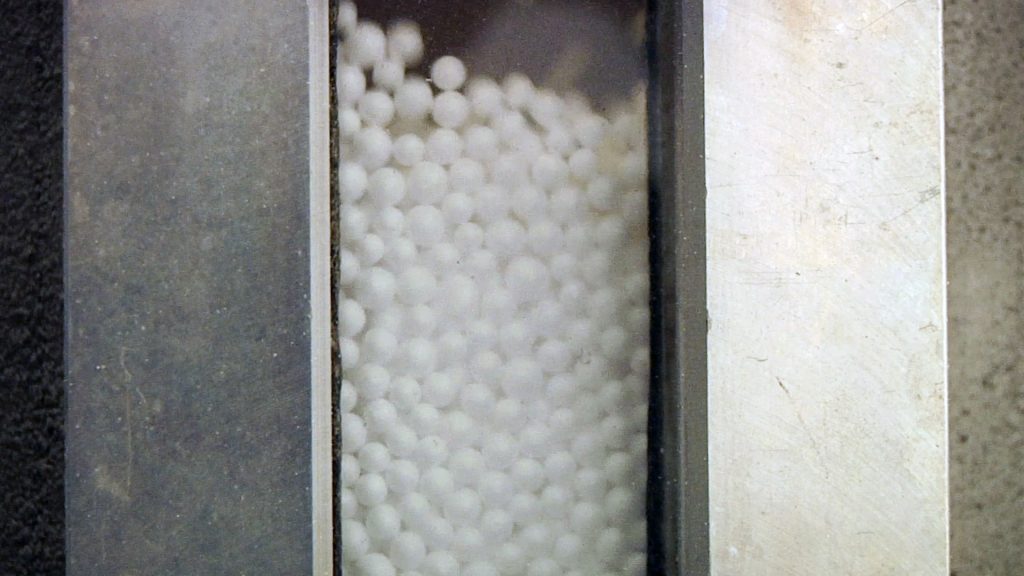

Pre-expansion:
The raw material is heated with steam at temperatures between 80°C and 100°C to create a uniform cellular structure with small closed cells that hold air in their interior.

Intermediate maturing and stabilization:
The beads’ internal gas expands, generating an air-penetrable cellular structure. In this phase, beads achieve greater mechanical elasticity and improved expansion capacity.
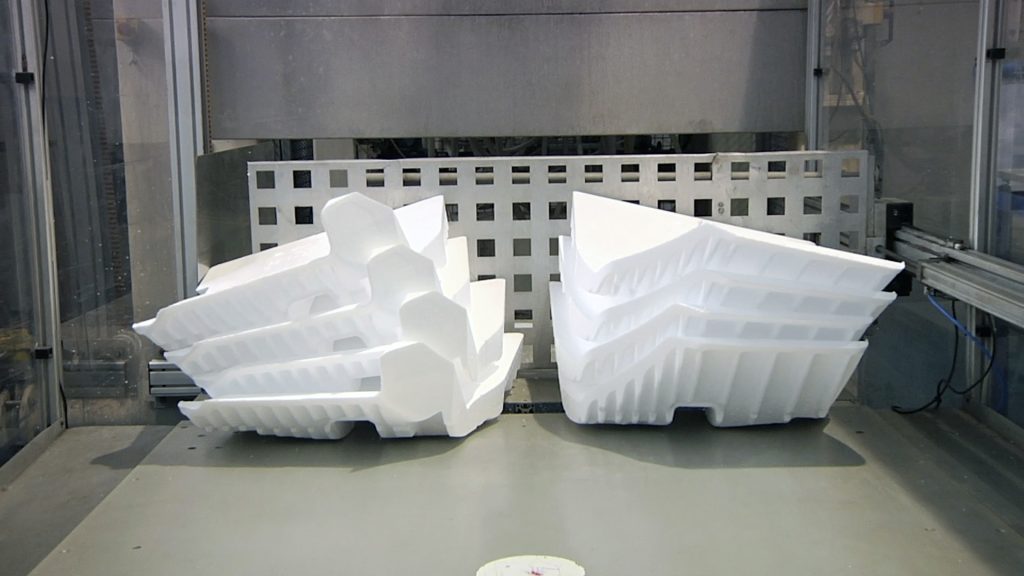
Expansion and final molding:
The stabilized pre-expanded cold beads are transported to specific moulds, where heat and mechanical force are applied again with the aim of welding them together and forming a solid block of EPS with the final desired shape.
Properties of EPS
EPS boasts a great number of outstanding properties that make it a privileged alternative to other plastics. Let’s give an overview of the most highlighted ones!

Recycling and Sustainability
Containing only 2% matter, EPS it is a 100% recyclable monomaterial. It also can be simply reused, contributing this way to a circular economy.
Besides, its lightweight allows easy handling, in addition to saving on transport costs, without losing any of its benefits in terms of cargo protection. This, in turn, results in a reduction in the carbon footprint and makes it an even more sustainable material.

Shock Absorption
Despite its low weight, EPS provides excellent protection against the feared impacts and vibrations that can put some loads in serious danger.
This is key, for example, when transporting pharmaceutical products or sensitive electronic devices, as well as for manufacturing interior technical parts for the automotive industry


Weight
Consisting in 98% air, it is extremely light and has a high strength-to-weight ratio. This is key for a variety of applications where heavier structures have been successfully substituted without compromising the safety of the system, for example, HVAC equipment or other technical parts.

Thermal and Acoustic Insulation
Due to the predominance of air in its composition, expanded polystyrene is an excellent thermal and acoustic insulator. This explains why it is extremely used in the rehabilitation of buildings with the aim to improve their energy efficiency and comfort.

History of EPS
Isolated for the first time
Discover high molecular weight polymers
Extruded foamed polystyrene
Developed and patented the expanded polystyrene
As in so many other cases, EPS broke into our lives by chance. More precisely, it was in 1839 when polystyrene was isolated for the first time from natural resin by the German apothecary Eduard Simon, even though he was not aware of the discovery.
It was not until 1922 when the also German organic chemist Hermann Staudinger, expressed his theories about polymers, stating that they were made up of long repetitive chains of monomers, which was the source of their elasticity. He also noted that materials made by heat treating styrene have characteristics similar to rubber and it was this point which led him to discover high molecular weight polymers, which include polystyrene.
The next decade was key to polystyrene: in 1930 the German chemical company BASF developed a way to manufacture polystyrene granules and in 1937 Dow Chemical invented extruded foamed polystyrene, being capable of manufacturing the first EPS products suitable for sale.
Finally, in 1951 BASF developed and patented the expanded polystyrene that we know as EPS then under the trademark Styropor®.
Nowadays, the global expanded polystyrene market is substantially growing year by year and it seems this upward tendency is not going to change in the mid term. In fact, the sector is expected to grow at a rate of 4.8% from now to 2028.
EPS Applications
Thanks to its outstanding properties, EPS has a wide range of applications, mainly in the four following industries:

Construction
Polystyrene is highly used in construction in a broad range of applications. The most highlighted ones are undoubtedly in terms of insulation, namely panel applications and HVAC systems components; and related to backfilling, as due to its lightness it enables to reduce the weight of embankments, especially on top of soft soil.
Other applications in this sector include decorative tiles and mouldings and foundations, where it is used as an aggregate in lightweight concrete.

Automotive
A sector focused on the search for solutions that lighten the weight of vehicles to reduce fuel consumption and polluting emissions like the automotive industry, has found in EPS a great ally due to its void filling capacity and the thermal and acoustic insulation it provides,
Precisely, it is used in the manufacture of numerous parts, such as mouldings, footrests, and in child safety seats. It is even useful for electric vehicles, as the lower the weight, the greater the autonomy.
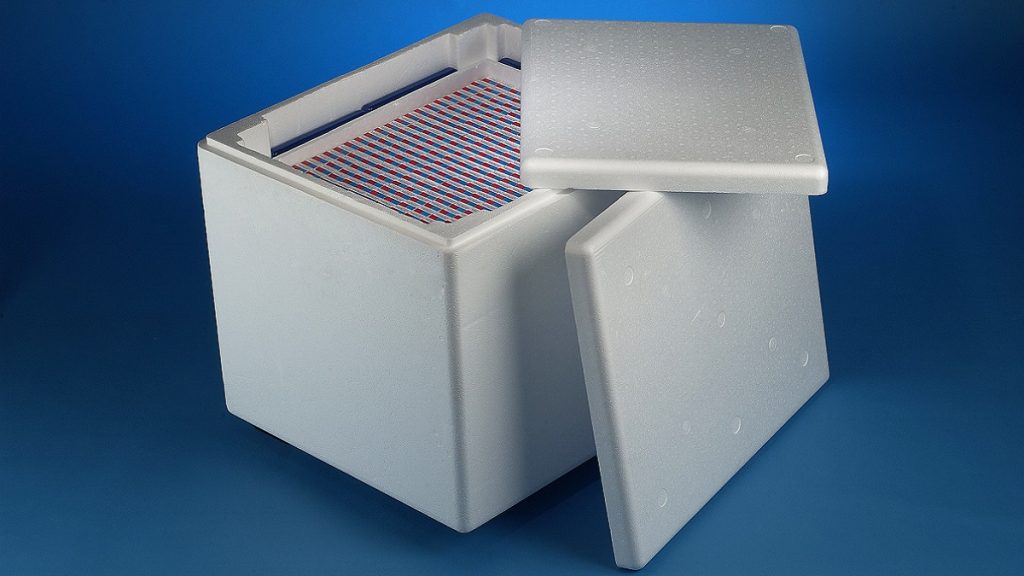
Pharmaceutical
Maintaining the cold chain is vital when transporting pharmaceutical products in order not to spoil them. In this regard, isothermal containers made with EPS are a great alternative for thermolabile medicaments among others.
EPS also stands out in terms of hygienics, as it prevents the growth of microorganisms. In this way, thermally insulating containers protect the products inside against processes such as decomposition and guarantee that they arrive in perfect safety conditions.

Agri-food
A fundamental condition in food containers is not to modify their content in any way. This is easy to accomplish with EPS, as it is an inert material, therefore, it does not transfer any substance to the element with which it is in contact.
Moreover, as an impact-resistant polymer capable of providing excellent thermal insulation, it keeps the organoleptic characteristics of food and its nutritional qualities unchanged for longer, avoiding food waste.
At Knauf Industries we go a step further as we offer the possibility to incorporate smart packaging functions into EPS packaging. Particularly, thanks to NFC or Bluetooth sensors, it is possible to monitor inputs such as temperature changes.
Our EPS Products
Knauf Industries has globally renowned expertise in moulded product design and manufacture, being EPS the most extensively used material together with EPS.
We offer a broad range of solutions, being the following some of the most highlighted ones:
Motor vehicle interior components:

Due to its impact resistance, sturdiness, soundproofing and chemical neutrality EPS is an excellent alternative.
EPS Agro Boxes:

They serve to minimise the negative consequences of impacts (which represents 14% of food shrinkage) and to protect the food from the sudden temperature changes by maintaining the cold chain.
Knauf GEOFOAM®:
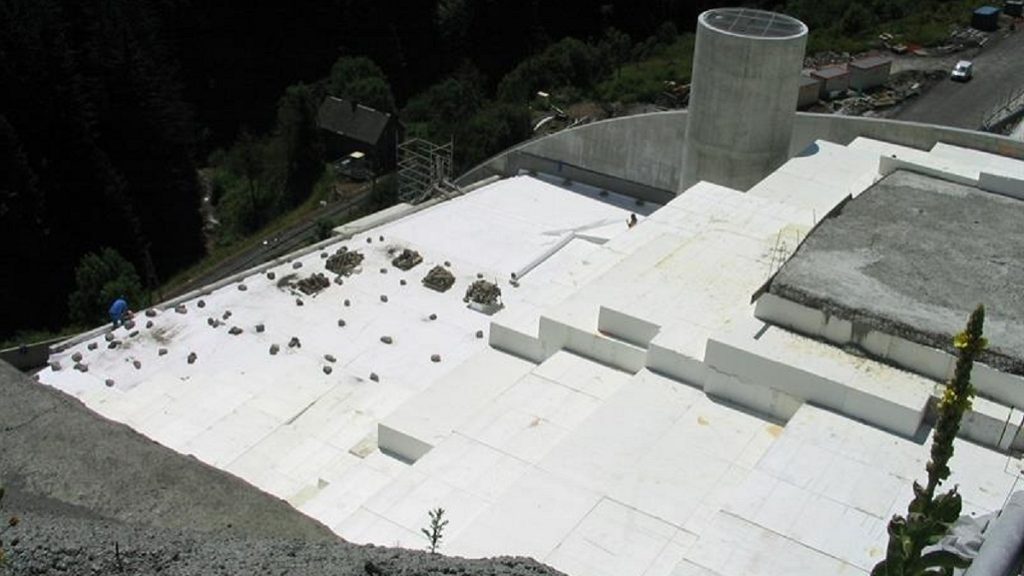

Our blocks made from EPS are perfect for building structures of great vertical and horizontal resistance thanks to its lightness. The volume occupied by the blocks makes them ideal for regrowth land, reducing earthmoving.
Isothermal containers FROBOX®:

Thanks to EPS insulating properties the temperature inside the packaging varies very slowly, more precisely, it takes 110 hours to go from -80ºC to -20ºC. It is especially indicated for the transport of solid CO2, known as dry ice, which is the key element to keep vaccines, among others, at the indicated temperature.